As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly common on roads around the world, understanding the basics of charging is more important than ever—especially for first-time EV owners. One of the most accessible and widely available charging methods is Level 1 EV charging, often considered the entry point to EV ownership.
Unlike high-speed public chargers or more complex home setups, Level 1 charging uses a standard household outlet—the same one you’d use for a phone charger or a microwave. It may not be the fastest method, but it offers unmatched convenience and zero installation cost. For many drivers, this basic form of charging is more than enough for daily commuting or overnight top-ups.
In this article, we’ll break down how Level 1 EV charging works, explore how long it takes to charge various EVs, and help you choose the best Level 1 chargers available today. Whether you’re considering your first electric car or simply want to better understand your current charging setup, this guide will give you all the essentials in a clear, practical format.
What Is Level 1 EV Charging?
Level 1 EV charging is the most basic and accessible method of charging an electric vehicle. It uses a standard household electrical outlet—typically 120 volts in North America or 220–240 volts in many other countries. This method requires no special installation and is often referred to as “plug-and-play” charging.
It’s the type of charger that usually comes included with most EVs at the time of purchase, allowing owners to charge their vehicle anywhere there’s a compatible outlet.
Level 1 charging involves plugging your electric vehicle into a standard AC power outlet using the portable charging cable provided by the manufacturer. These chargers typically deliver around:
- 120 volts / 12–16 amps in North America
- Up to 1.9 kW of power output
- Charging speed: ~3–5 miles (5–8 kilometers) of range per hour
While this charging rate is relatively slow, it’s often sufficient for overnight charging or for users with short daily commutes.
Voltage and Power Output
Unlike Level 2 or DC fast charging, Level 1 operates on basic home voltage and does not require additional wiring or hardware. Here’s how it compares:
| Charging Level | Voltage | Power Output | Charging Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 120V | 1.3–1.9 kW | 3–5 miles/hour |
| Level 2 EV Charging | 240V | 3.3–19.2 kW | 15–40 miles/hour |
| DC Fast Charging | 400V+ | 50–350 kW | 100+ miles in 30 min |
Note: The exact speed depends on your vehicle’s battery capacity, onboard charger, and current battery level.
Common Use Cases for Level 1 Charging
Despite being the slowest charging option, Level 1 remains a practical choice in several situations:
- Home charging overnight: Perfect for people who drive 30–40 miles/day and have 8+ hours to recharge.
- Urban or apartment dwellers: If access to public or wall-mounted Level 2 charging is limited.
- PHEV owners: Plug-in hybrids with smaller batteries can be fully recharged overnight.
- Emergency backup: A reliable fallback charging option when other chargers are unavailable.
Level 1 vs Level 2: Key Differences
(Brief mention here, full comparison in later section.)
| Feature | Level 1 | Level 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Outlet Type | Standard 120V | 240V (requires dedicated line) |
| Charging Speed | Slow | Medium to Fast |
| Installation Required | No | Yes |
| Ideal For | PHEVs, short-range use | Daily BEV charging |
Who Can Use Level 1 Charging? Compatibility by EV Type
While Level 1 EV charging is widely available and technically simple, it’s not universally compatible with all types of electric vehicles. Here’s how Level 1 charging applies to the different EV categories:
BEVs
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are fully electric vehicles that rely 100% on battery power. Level 1 charging works with BEVs, but the process is slow due to the larger battery capacity—often 60 kWh or more. It may take 20 to 50 hours to fully charge depending on the model. For BEV owners, Level 1 is best used as a backup or overnight trickle charge, especially if daily mileage is low.
PHEVs
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) combine an internal combustion engine with a small rechargeable battery. Most have battery capacities between 8 to 18 kWh, making Level 1 charging a perfect match. You can fully charge a PHEV in 4 to 8 hours using a regular wall outlet, typically overnight.
HEVs
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) like the Toyota Prius (non-plug-in version) cannot be charged using an external charger. Their small battery is charged automatically through regenerative braking and the engine. Level 1 charging does not apply to this category.
FCEVs
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) use hydrogen fuel cells instead of batteries to generate electricity. Since they don’t store electricity in the same way, Level 1 (or any plug-in charging) is not compatible with FCEVs.
Compatibility Table
| EV Type | Compatible with Level 1 Charging? | Charging Time Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| BEV | Yes (but slow) | 20–50 hours (full charge) |
| PHEV | Yes (ideal) | 4–8 hours |
| HEV | No | Not applicable |
| FCEV | No | Not applicable |
This breakdown helps you determine whether Level 1 charging makes sense for your EV. For most plug-in hybrids and light daily use of BEVs, it’s a cost-effective and simple solution.
How Level 1 EV Charging Works
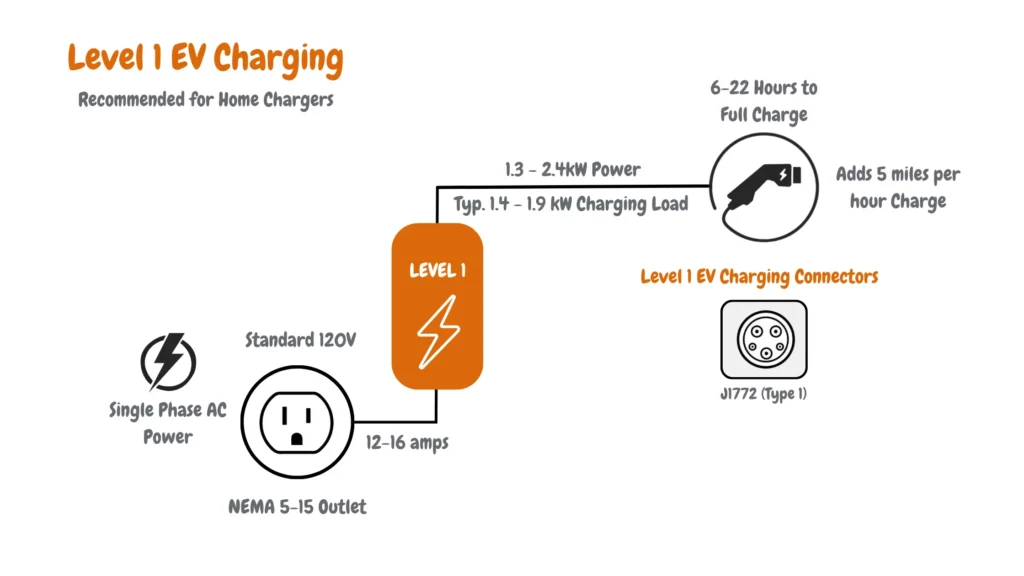
Level 1 EV charging works by delivering alternating current (AC) electricity from a standard wall outlet directly to the vehicle’s onboard charger. The onboard charger then converts that AC power into direct current (DC) to store in the vehicle’s battery. Because Level 1 chargers operate at low power levels, this process is simple, slow, and requires minimal infrastructure.
This charging method is considered “trickle charging” because it transfers energy gradually. Despite its slow speed, it is remarkably reliable and convenient—especially for overnight use or vehicles with smaller batteries.
The Charging Process Step by Step
- Plug Into a Standard Outlet: A Level 1 charger uses a typical 120-volt (in North America) or 220–240-volt (in many other countries) outlet. No dedicated charging station is required.
- Connect to the Vehicle’s Charging Port: The plug is inserted into the EV’s charging inlet. Most EVs use standard connectors (like SAE J1772 in North America).
- AC to DC Conversion Inside the Car: Once connected, the vehicle’s onboard charger converts incoming AC to DC, allowing it to charge the battery pack.
- Slow but Steady Power Flow: Charging proceeds at a rate of around 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. The process can take several hours to fully charge a battery, especially in larger BEVs.
- Automatic Stop When Fully Charged: The vehicle’s battery management system will automatically stop the charging process when the battery reaches full capacity, preventing overcharging.
Connection Type: Standard Wall Outlet (NEMA 5-15)
In North America, Level 1 charging typically uses a NEMA 5-15 outlet, the same three-prong outlet found in almost every home. These outlets deliver around 12 amps of current at 120 volts, providing roughly 1.4 to 1.9 kilowatts of power.
For other regions (like Europe or Asia), household voltage is generally 220–240V, which allows for slightly faster Level 1 charging speeds, although the principle remains the same.
There’s no need for any special installation or electrician unless the existing outlet is outdated or not rated for continuous load.
Onboard Charger Compatibility and Limitations
The onboard charger in every EV determines how much power the vehicle can accept from a given source. While Level 1 chargers are universally compatible, the onboard charger controls:
- Maximum charging rate
- Battery safety
- Power management
Limitations to keep in mind:
- Charging time can exceed 24–50 hours for a full charge in large-battery EVs.
- Outdoor charging may require weatherproof cables or outlets.
- Plugging into an old or overloaded outlet may trip breakers or pose safety risks.
For these reasons, while Level 1 charging is widely usable, it’s most effective for:
- Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs)
- Urban users with low daily mileage
- Occasional charging needs or backup scenarios
Charging Time with Level 1
One of the most common questions about Level 1 EV charging is: How long does it take? Since this method delivers a relatively low amount of power, charging times can vary significantly depending on the vehicle, the battery size, and how much range is needed.
While Level 1 charging is the slowest option available, it can still be useful—especially for overnight charging, light commuting, or plug-in hybrids with smaller batteries.
Average Charging Rate per Hour
Level 1 chargers typically deliver 1.4 to 1.9 kilowatts (kW) of power, which translates into an average range gain of:
- 3 to 5 miles of driving range per hour
- 5 to 8 kilometers per hour in metric terms
This means that charging your EV for 8 hours overnight can provide approximately:
- 24 to 40 miles of additional range
- Sufficient for daily use if your commute is under 30 miles per day
Estimated Full Charge Time for Common EV Models
Here’s a comparison of estimated full charging times using a standard Level 1 charger:
| EV Model | Battery Size (kWh) | Level 1 Charging Time (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Chevrolet Bolt EV | 65 kWh | 40–50 hours |
| Tesla Model 3 Standard Range Plus | 54 kWh | 35–45 hours |
| Nissan Leaf (40 kWh) | 40 kWh | 25–35 hours |
| Hyundai Kona Electric | 64 kWh | 40–50 hours |
| Toyota Prius Prime (PHEV) | 8.8 kWh | 5–7 hours |
| Ford Escape Plug-in Hybrid | 14.4 kWh | 8–10 hours |
Note: These are estimates based on average charging power of ~1.5 kW. Real-world times may vary depending on charging conditions, state of charge, temperature, and the vehicle’s onboard charger.
Factors Affecting Level 1 Charging Time
Several variables can impact how fast your EV charges using a Level 1 outlet:
1. Battery Size
Larger batteries take longer to charge. For example, a 70 kWh battery will take significantly longer than a 15 kWh battery.
2. Current Battery Level
Charging from 0% to 100% takes the longest. Most users rarely let their EV drain completely, so partial charges are more typical.
3. Charging Efficiency
Some energy is lost during the charging process. More efficient onboard chargers can reduce total time slightly.
4. Ambient Temperature
Very cold or hot weather can slow down charging or limit battery acceptance rates to protect battery health.
5. Voltage Stability and Outlet Quality
Low-quality or old wiring may reduce the effective power flow, slowing the charge or triggering safety cutoffs.
When Is Level 1 Charging Practical?
Level 1 charging may be slow, but it’s still useful in many situations:
- Overnight home charging for short commutes
- Charging plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) efficiently
- Backup option when Level 2 or public chargers are unavailable
- Cost-saving scenarios where time is not a concern
For drivers who travel less than 40 miles a day and have reliable access to an outlet, Level 1 can fully meet daily driving needs without any additional infrastructure costs.
Pros and Cons of Level 1 EV Charging
Level 1 charging offers an accessible and low-cost way to charge an electric vehicle, especially at home. But it’s not without its limitations. Depending on your driving habits, vehicle type, and living situation, Level 1 may be either an ideal solution or a daily inconvenience.
Here’s a breakdown of the major advantages and disadvantages to help you decide if Level 1 EV charging fits your needs.
Advantages of Level 1 Charging
1. No Installation Required
Level 1 chargers plug into standard household outlets (NEMA 5-15 in North America), so there’s no need to hire an electrician or install new infrastructure. It’s ready to use out of the box.
2. Low Upfront Cost
Since the charger is often included with the vehicle and uses existing electrical outlets, Level 1 is the most cost-effective way to begin charging at home.
3. Ideal for PHEVs and Low Daily Mileage
For plug-in hybrids or drivers with short daily commutes, Level 1 charging provides enough range with overnight sessions.
4. Simple and Portable
Level 1 chargers are compact and easy to transport, making them suitable for travel, emergencies, or use in multiple locations.
5. Safe and Slow Charging
Because of its low power output, Level 1 charging reduces battery heat and stress, which can extend long-term battery health.
Disadvantages of Level 1 Charging
1. Very Slow Charging Speeds
Charging at only 3–5 miles of range per hour, Level 1 is often too slow for full electric vehicles (BEVs) with large batteries—especially if you need quick turnarounds.
2. Limited Use for High-Distance Drivers
Drivers who regularly travel more than 50 miles per day may find Level 1 inadequate for daily needs without supplementing with faster options.
3. Dependent on Outlet Availability
Using an outdoor outlet or extension cord may require additional safety precautions. Shared or apartment living can also limit access.
4. Not Scalable for Multiple EVs
Households with more than one EV will likely need faster charging options to keep all vehicles ready without scheduling conflicts.
5. Long Full-Charge Times
For full BEVs, a complete charge may take 30–50 hours—far from practical if the battery is frequently depleted.
When Level 1 Charging Still Makes Sense
Despite its limitations, Level 1 charging remains practical for several use cases:
- PHEV owners who only need 8–10 kWh per day
- Apartment dwellers who have limited charging options
- Drivers with consistent overnight parking
- New EV owners looking to avoid upfront costs of Level 2 setups
- As a backup for emergencies or travel
If your driving habits align with its capabilities, Level 1 charging offers a simple, low-barrier entry into electric mobility.
Level 1 EV Chargers: What to Look For
Choosing the right Level 1 EV charger can make a significant difference in your daily charging experience. While many electric vehicles come with a standard Level 1 charging cable, not all chargers are created equal. Some offer better safety features, higher build quality, and added convenience for long-term use.
If you’re considering an upgrade or a replacement, here are the key features and considerations to help you choose the most reliable and effective Level 1 charger.
Key Specs to Consider
When comparing Level 1 EV chargers, pay attention to the following specifications:
1. Amperage Rating
Most Level 1 chargers operate between 12 to 16 amps. Higher amperage allows for slightly faster charging, but ensure your outlet and wiring can safely support the load.
2. Voltage
Level 1 charging uses 120 volts in North America (or 220–240 volts in other regions). This is standard household power, so any Level 1 charger should match your region’s voltage supply.
3. Power Output
A good charger should consistently deliver 1.4 to 1.9 kW, depending on amperage and voltage. Consistency matters for long overnight charging sessions.
4. Cable Length
Longer cables (20–25 feet) provide more flexibility, especially if your vehicle is parked a distance from the outlet.
5. Port Compatibility
Ensure the plug uses the SAE J1772 connector, which is standard for most EVs in North America. Tesla drivers will need an adapter.
Safety Features to Look For
Reliable Level 1 chargers should have certifications and built-in protection mechanisms to ensure safe operation:
- UL Listed or ETL Certified: Indicates compliance with electrical safety standards.
- Overcurrent and Overvoltage Protection: Prevents damage to the charger and vehicle.
- Temperature Monitoring: Reduces risk of overheating during prolonged charging.
- Weatherproofing: Especially important for outdoor use (look for IP65 or higher ratings).
- Automatic Shutoff: Stops charging when the battery is full or if there’s a power interruption.
A good charger will protect both your car and your home’s electrical system.
Top Level 1 EV Chargers in 2025
Here are some of the best-rated and widely trusted Level 1 chargers available as of 2025. These are compatible with most EVs and offer solid performance for home use.
| Charger Model | Amperage | Cable Length | Notable Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lectron Level 1 Charger | 16A | 21 ft | UL Certified, LED indicators | $160–$190 |
| Emporia EV Charger (Level 1/2 hybrid) | 16A (on 120V) | 24 ft | Wi-Fi app, NEMA 5-15 plug | $180–$210 |
| PRIMECOM Level 1 Charger | 16A | 25 ft | LCD screen, temperature sensors | $200–$230 |
| Schumacher SC1455 | 15A | 28 ft | Rugged build, weatherproof | $130–$160 |
| BougeRV Level 1 Portable Charger | 15A | 25 ft | ETL listed, portable case | $140–$170 |
Note: Prices may vary by region and availability. Always check compatibility with your specific vehicle before purchasing.
Should You Upgrade Your Stock Charger?
Most EVs come with a basic Level 1 charger. However, upgrading may be worthwhile if:
- You need a longer cable or outdoor durability
- You want faster charging within Level 1 limits
- You prefer added safety features or smart monitoring
An aftermarket charger can provide better reliability, safer performance, and greater convenience.
Conclusion
Level 1 EV charging may be the simplest and slowest form of electric vehicle charging—but for many drivers, it’s also the most practical. By using a standard household outlet and requiring no installation, it provides a low-cost, low-barrier entry into electric driving. While it’s not the fastest option, its convenience and accessibility make it an excellent starting point, especially for:
- Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) owners
- Drivers with short daily commutes
- EV users with overnight parking access
- First-time EV owners testing the waters before investing in Level 2
However, if your lifestyle includes frequent long-distance driving, multiple EVs in the household, or you simply want faster turnaround times, Level 2 charging may be a better long-term solution.
The most important consideration is your daily energy usage. If you can consistently recover the range you use within the time your vehicle is parked, Level 1 charging is more than adequate. It’s reliable, easy to use, and often overlooked as a long-term solution for light-duty EV usage.
By understanding its capabilities, limitations, and compatibility, you can confidently decide whether Level 1 charging fits your EV lifestyle—or whether it’s time to upgrade.
FAQ About Level 1 EV Charging
To help clarify common concerns and uncertainties, here are answers to frequently asked questions about Level 1 EV charging. Whether you’re a first-time EV owner or just exploring your charging options, these FAQs offer quick insights that can help guide your decisions.
Can I Use Level 1 Charging Every Day?
Yes. For many EV owners—especially those with plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) or short daily commutes—Level 1 charging is sufficient for everyday use. If your vehicle adds 3–5 miles of range per hour and you’re plugged in for 8–10 hours overnight, you can easily recover 25–40 miles of range per day.
However, for full battery electric vehicles (BEVs) with larger batteries and longer commutes, Level 1 charging may not replenish energy fast enough to keep up with daily needs.
Is It Safe to Charge an EV Using a Regular Wall Outlet?
Yes, Level 1 charging is generally safe if the outlet and wiring are in good condition. Always follow these precautions:
Use a dedicated outlet that isn’t shared with other appliances
Avoid using extension cords or adapters not rated for continuous charging
Ensure the outlet is grounded and properly installed
Look for chargers with UL or ETL certification for added safety
If you live in an older home, you may want to consult an electrician to verify the circuit’s capacity and safety.
Can I Charge in Bad Weather?
Yes, but make sure your charging setup is designed for outdoor use. Many Level 1 chargers are weatherproof, but it’s important to:
Use chargers with IP65 or higher ratings
Avoid submerging connectors or plugs in standing water
Ensure the outlet itself is covered or sheltered from rain
Modern EVs and chargers are built with multiple safety layers to protect against environmental hazards, but it’s still wise to take precautions in extreme conditions.
Can I Upgrade to Level 2 Later?
Absolutely. Many EV owners start with Level 1 charging, then upgrade to Level 2 when:
Their daily mileage increases
They buy a second EV
They install a home charging station
Level 2 charging requires a 240V outlet and often professional installation, but it dramatically reduces charge times and is ideal for full EVs or households with multiple electric vehicles.
Importantly, starting with Level 1 gives you a low-cost, low-risk entry into EV ownership without major infrastructure investment.
Does Level 1 Charging Damage My Battery?
No. Level 1 charging is actually considered gentle on EV batteries due to its slow, steady current. In fact, some experts argue that slower charging generates less heat and reduces long-term stress on battery cells.
Battery degradation is more commonly influenced by:
Extreme heat or cold
Fast charging too frequently (e.g., DC fast charging)
Constant full charges or deep discharges
As long as you’re charging within the recommended limits, Level 1 is among the least stressful charging methods available.




